반응형

a. 다차원 배열을 만들거라면 [][]를 함께 작성해야 한다.
b. 맞다. int arr[] = {1,2,3}; 으로도 되지만 3 이후에 , 을 작성해도 에러가 뜨지 않음
c. 배열의 길이 먼저 작성할 것
d. 배열의 길이와, 배열 내부의 요소들을 함께 작성할 수 없다.
e. 선언과 동시에 배열 객체를 생성하거나, 바로 요소를 입력해야 한다.
int[] arr = new int[5] ; 또는 int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
f. 다차원 배열 쓰다마는 것 불가능

arr[3] 은 {30, 30} 이므로 length (길이) 는 2
답 : 2
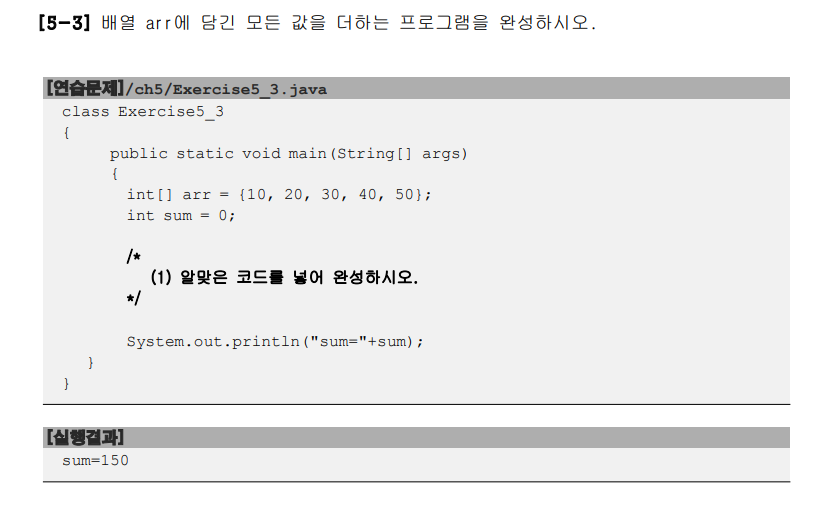
답 :
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
package ch05;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
System.out.println("sum="+sum);
}
}
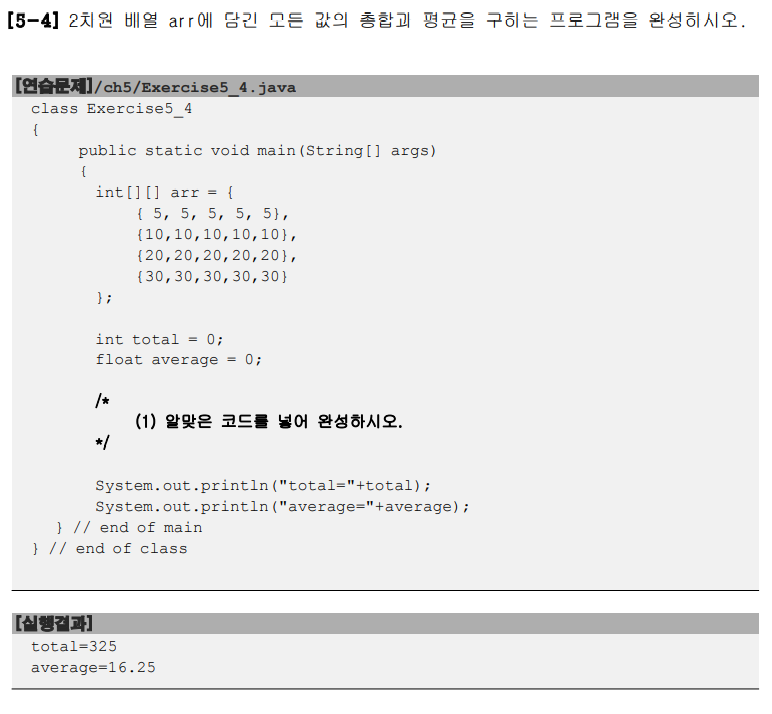
package ch05;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = {
{ 5, 5, 5, 5, 5},
{10,10,10,10,10},
{20,20,20,20,20},
{30,30,30,30,30}
};
int total = 0;
float average = 0;
int num = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
total += arr[i][j];
num++;
}
}
average = total/(float)num;
System.out.println("total="+total);
System.out.println("average="+average);
}
}

package ch05;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ballArr = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int[] ball3 = new int[3];
// ballArr . 배열 의 임의의 요소를 골라서 위치를 바꾼다
for(int i=0; i< ballArr.length; i++) {
int j = (int)(Math.random() * ballArr.length);
int tmp = 0;
tmp = ballArr[i];
ballArr[i] = ballArr[j];
ballArr[j] = tmp;
}
// ballArr의 앞에서 3개의 수를 배열 ball3로 복사한다.
ball3 = Arrays.copyOfRange(ballArr, 0, 3);
for(int i=0;i<ball3.length;i++) {
System.out.print(ball3[i]);
}
}
}
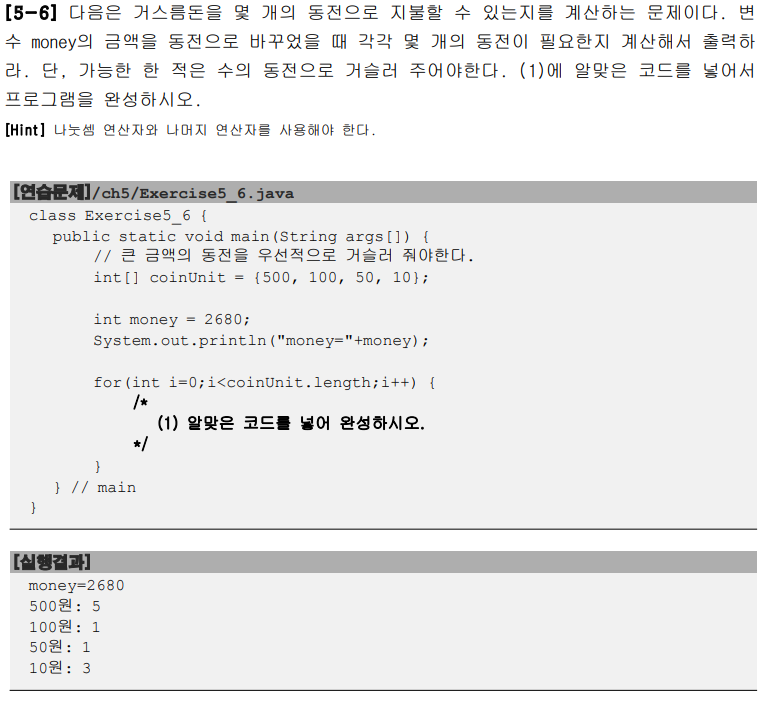
package ch05;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] coinUnit = {500, 100, 50, 10};
int money = 2680;
System.out.println("money="+money);
// int[] change = new int[4];
for(int i=0; i < coinUnit.length; i++) {
int num = money/coinUnit[i];
money = money%coinUnit[i];
System.out.printf("%d원: %d %n", coinUnit[i], num);
}
}
}

이해가 안감..
package ch05;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(args.length!=1) {
System.out.println("USAGE: java Exercise5_7 3120");
System.exit(0);
}
// 1. 문자열을 숫자로 변환한다 입력한 값이 숫자가 아닐 경우 예외가 발생한다
int money = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
System.out.println("money="+money);
int[] coinUnit = {500, 100, 50, 10 }; // 동전의 단위
int[] coin = {5, 5, 5, 5}; // 단위별 동전의 개수
for(int i=0;i<coinUnit.length;i++) {
int coinNum = 0;
coinNum = money/coinUnit[i];
System.out.println("COINNUM: " + coinNum);
if(coinNum > coin[i]) {
}
money = money%coinUnit[i];
System.out.println("money: " + money);
System.out.println(coinUnit[i]+"원: "+coinNum);
}
if(money > 0) {
System.out.println("거스름돈이 부족합니다.");
System.exit(0); // 프로그램을 종료한다
}
System.out.println("=남은 동전의 개수 =");
for(int i=0;i<coinUnit.length;i++) {
System.out.println(coinUnit[i]+"원 :"+coin[i]);
}
}
}
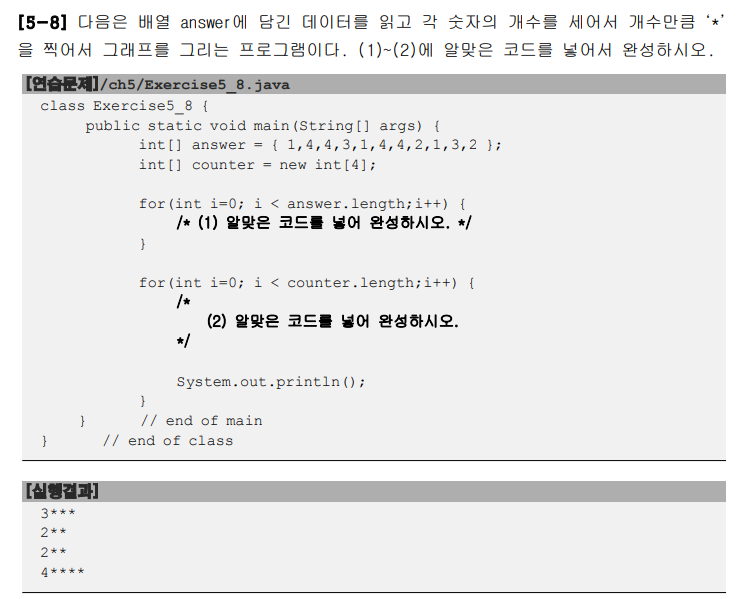
switch 문을 이용했다.
package ch05;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] answer = { 1,4,4,3,1,4,4,2,1,3,2 };
int[] counter = new int[4];
for(int i=0; i < answer.length;i++) {
switch(answer[i]) {
case 1: counter[0]++;
break;
case 2: counter[1]++;
break;
case 3: counter[2]++;
break;
case 4: counter[3]++;
break;
}
}
for(int i=0; i < counter.length;i++) {
System.out.print(counter[i]);
for(int j = 0; j < counter[i]; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}

package ch05;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[][] star = {
{ '*', '*', ' ', ' ', ' ' },
{ '*', '*', ' ', ' ', ' ' },
{ '*', '*', '*', '*', '*' },
{ '*', '*', '*', '*', '*' }
};
char[][] result = new char[star[0].length][star.length];
for (int i = 0; i < star.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < star[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(star[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
// 4행 5열 > 5행 4열
// star - 00 10 20 30 을
// result - 00 01 02 03
//
for (int i = 0; i < star.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < star[i].length; j++) {
int k = 0;
if(i == 0) {
k = 3;
} else if(i == 1) {
k = 2;
} else if(i == 2) {
k = 1;
} else if(i == 3) {
k = 0;
}
result[j][k] = star[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < result[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(result[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
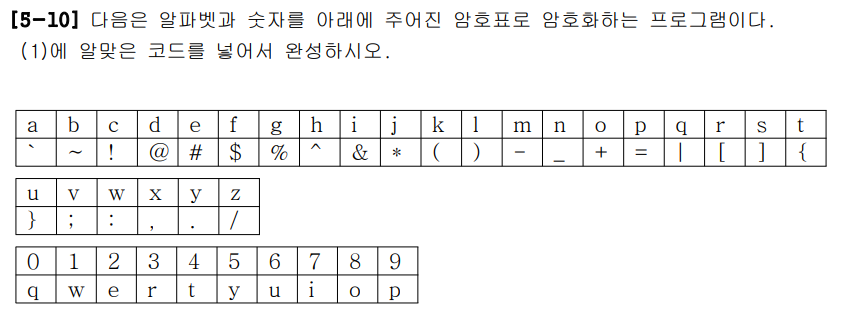
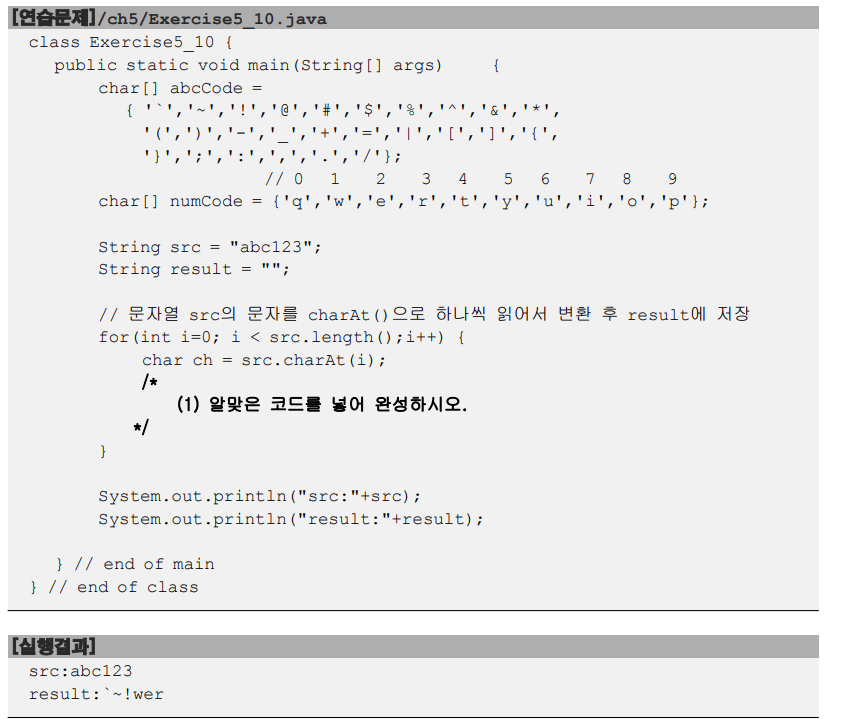
package ch05;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] abcCode = {
'`', '~', '!', '@', '#', '$', '%', '^', '&', '*', '(', ')', '-', '_', '+', '=', '|', '[',
']', '{', '}', ';', ':', ',', '.', '/' };
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
char[] numCode = { 'q', 'w', 'e', 'r', 't', 'y', 'u', 'i', 'o', 'p' };
String src = "abc123";
String result = "";
// src charAt() result 문자열 의 문자를 으로 하나씩 읽어서 변환 후 에 저장
for (int i = 0; i < src.length(); i++) {
char ch = src.charAt(i);
//알파벳인지 확인
if(ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
result+= abcCode[ch-'a'];
} else if(ch >= '1' && ch <= '9') { //아니라면
result+= numCode[ch-'0'];
}
}
System.out.println("src:" + src);
System.out.println("result:" + result);
}
}

package ch05;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] score = {
{ 100, 100, 100 },
{ 20, 20, 20 },
{ 30, 30, 30 },
{ 40, 40, 40 },
{ 50, 50, 50 }
};
int[][] result = new int[score.length + 1][score[0].length + 1];
int total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
int sum = 0;
int sum1 = 0;
int sum2 = 0;
int sum3 = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < score[i].length; j++) {
sum += score[i][j];
result[i][j] = score[i][j];
total += score[i][j];
result[i][j+1] = sum;
if(j == 0) {
sum1 = score[i][j];
result[result[i].length+1][j] += sum1;
} else if(j == 1) {
sum2 = score[i][j];
result[result[i].length+1][j] += sum2;
} else if(j == 2) {
sum3 = score[i][j];
result[result[i].length+1][j] += sum3;
}
if(j == score[i].length-1) {
result[5][3] = total;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < result[i].length; j++) {
System.out.printf("%4d", result[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
쉬운 방법으로 다시 풀어봐야겠다

package ch05;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Quiz {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
String[][] question = {
{"chair", "의자"},
{"computer", "컴퓨터"},
{"integer", "정수"}
};
int correct = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < question.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("'%s'의 뜻은 무엇입니까? ", question[i][0]);
String answer = scn.nextLine();
if(answer.equals(question[i][1])) {
System.out.println("정답입니다.");
correct++;
} else {
System.out.printf("오답입니다. 정답은 '%s'입니다. %n", question[i][1]);
}
if(i == question.length-1) {
System.out.printf("전체 문제 %d문제 중에 %d문제 맞추셨습니다.", question.length ,correct);
}
}
}
}
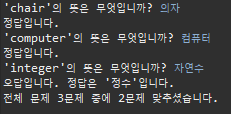

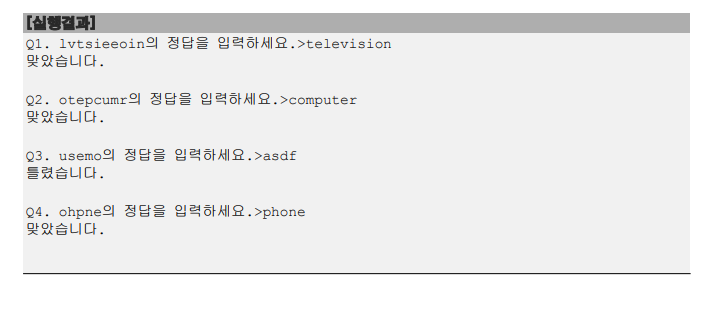
정답 부분
로또 만들기처럼 랜덤으로 섞는다
for(int j = 0; j < question.length; j++) {
int random = (int)(Math.random()*question.length);
char tmp = question[j];
question[j] = question[random];
question[random] = tmp;
}
전체
package ch05;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RandomChar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] words = { "television", "computer", "mouse", "phone" };
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=0;i<words.length;i++) {
char[] question = words[i].toCharArray(); // String char[] 을 로 변환
for(int j = 0; j < question.length; j++) {
int random = (int)(Math.random()*question.length);
char tmp = question[j];
question[j] = question[random];
question[random] = tmp;
}
System.out.printf("Q%d. %s의 정답을 입력하세요. >", i+1, new String(question));
String answer = scanner.nextLine();
// trim() answer , equals word[i] 으로 의 좌우 공백을 제거한 후 로 와 비교
if(words[i].equals(answer.trim()))
System.out.printf("맞았습니다. %n%n");
else
System.out.printf("틀렸습니다. %n%n");
}
}
}
반응형
'자바의정석' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자바의 정석 - 기초편] ch6-2~4 클래스와객체 (0) | 2022.03.07 |
|---|---|
| [자바의 정석 - 기초편] ch6-1 객체지향 언어 (0) | 2022.03.07 |
| [자바의 정석 - 기초편] ch5-24 Arrays로 배열 다루기 (0) | 2022.03.03 |
| [자바의 정석 - 기초편] ch5-21~23 2차원배열 예제 (0) | 2022.03.03 |
| [자바의 정석 - 기초편] ch5-18~20 2차원 배열 (0) | 2022.03.03 |