반응형


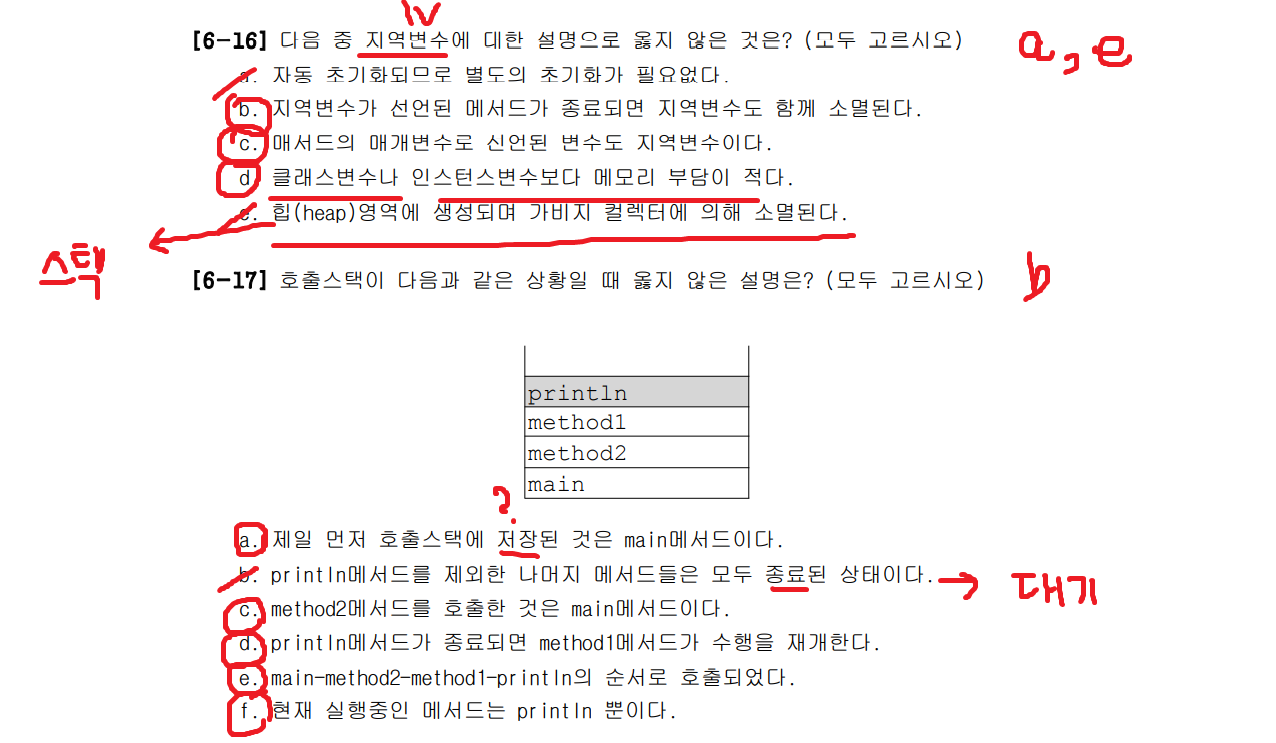
지역변수는 자동 초기화 되지 않기 때문에 사용하기 전에 반드시 적절한 값으로 초기화를 해주어야 한다. 지역변수는 자신이 선언된 블럭이나 메서드가 종료되면 소멸되므로 메모리 부담이 적다.
힙 영역에는 인스턴스 인스턴스변수 가 생성되는 영역이며,
지역변수는 호출스택 에 생성된다 (call stack) .


package ch06;
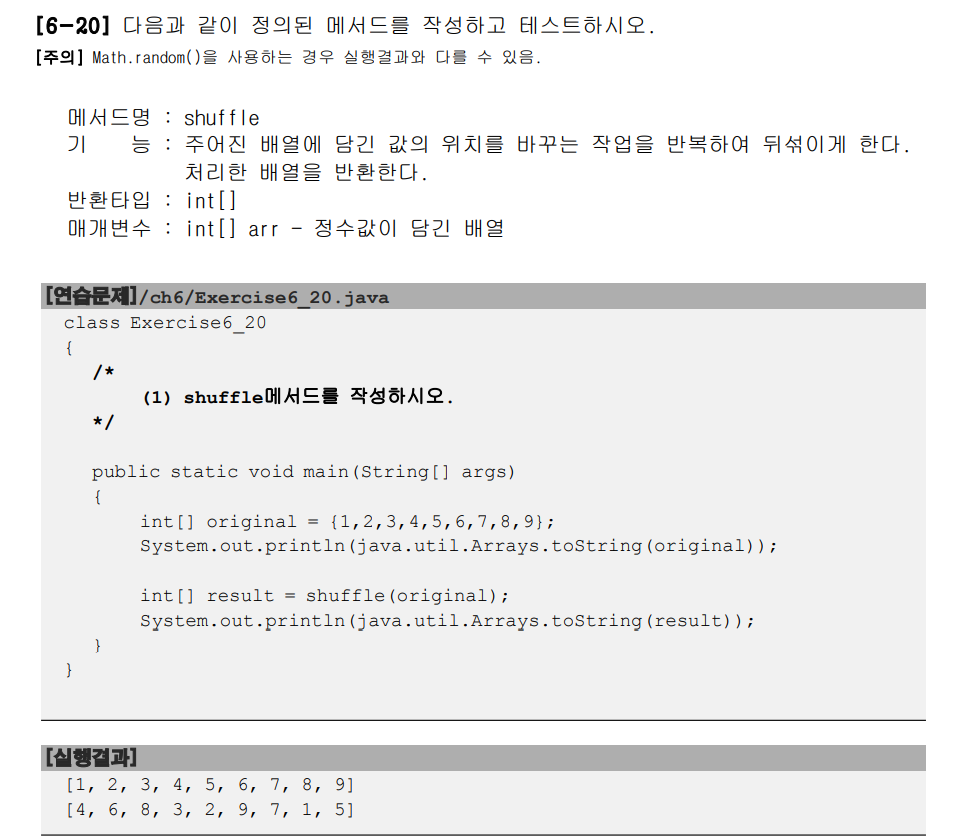
public class Exercise6_20 {
static int[] shuffle(int[] arr) {
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int j = (int)(Math.random()*arr.length);
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
return arr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] original = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
System.out.println(java.util.Arrays.toString(original));
int[] result = shuffle(original);
System.out.println(java.util.Arrays.toString(result));
}
}


package ch06;
public class Exercise6_21 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTv t = new MyTv();
t.channel = 100;
t.volume = 0;
System.out.println("CH:" + t.channel + ", VOL:" + t.volume);
t.channelDown();
t.volumeDown();
System.out.println("CH:" + t.channel + ", VOL:" + t.volume);
t.volume = 100;
t.channelUp();
t.volumeUp();
System.out.println("CH:" + t.channel + ", VOL:" + t.volume);
}
}
class MyTv {
boolean isPowerOn;
int channel;
int volume;
final int MAX_VOLUME = 100;
final int MIN_VOLUME = 0;
final int MAX_CHANNEL = 100;
final int MIN_CHANNEL = 1;
void turnOnOff() {
isPowerOn = !isPowerOn;
}
void volumeUp() {
if(volume < MAX_VOLUME)
volume++;
}
void volumeDown() {
if(volume > MIN_VOLUME)
volume--;
}
void channelUp() {
if(channel == MAX_VOLUME) {
channel = MAX_VOLUME;
} else {
channel++;
}
}
void channelDown() {
if(channel == MIN_VOLUME) {
channel = MIN_VOLUME;
} else {
channel--;
}
}
}
package ch06;
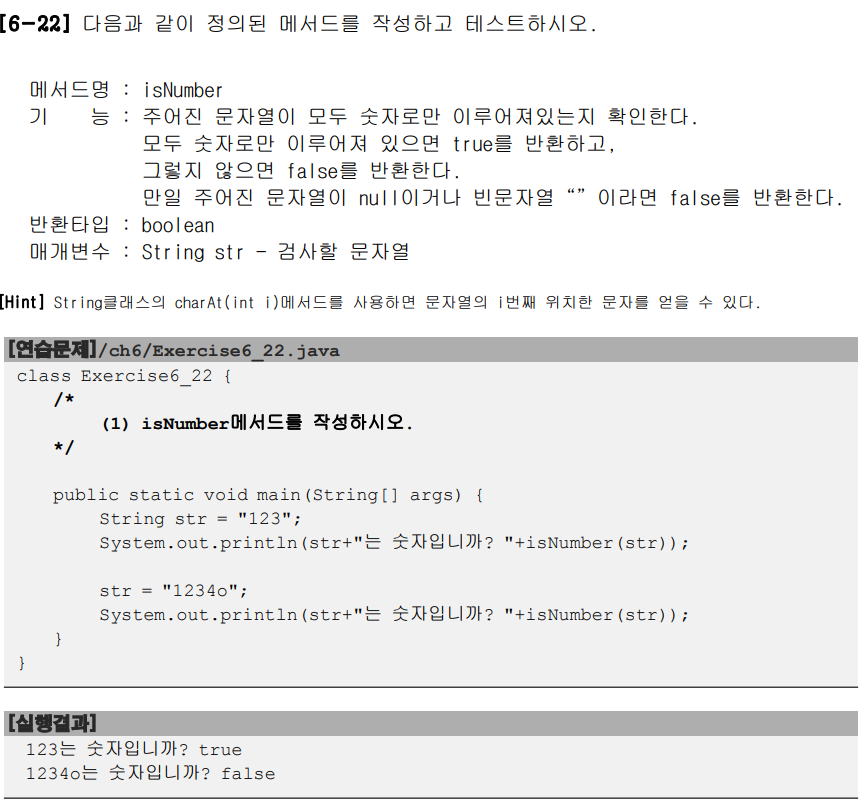
public class Exercise6_22 {
static boolean isNumber(String str) {
boolean isNumber = true;
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if(!(str.charAt(i) >= '0' && str.charAt(i) <= '9')) {
isNumber = false;
}
}
return isNumber;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "123";
System.out.println("str은 숫자입니까? " + isNumber(str));
String str2 = "1sb";
System.out.println("str은 숫자입니까? " + isNumber(str2));
}
}

package ch06;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Exercise6_23 {
static int max(int arr[]) {
if(arr.length == 0 || arr == null) {
return -999999;
}
int max = arr[0];
for(int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(max < arr[i]) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
return max;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[10];
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = (int)(Math.random()*arr.length);
}
System.out.println("arr배열: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
System.out.println(max(arr));
}
}
package ch06;
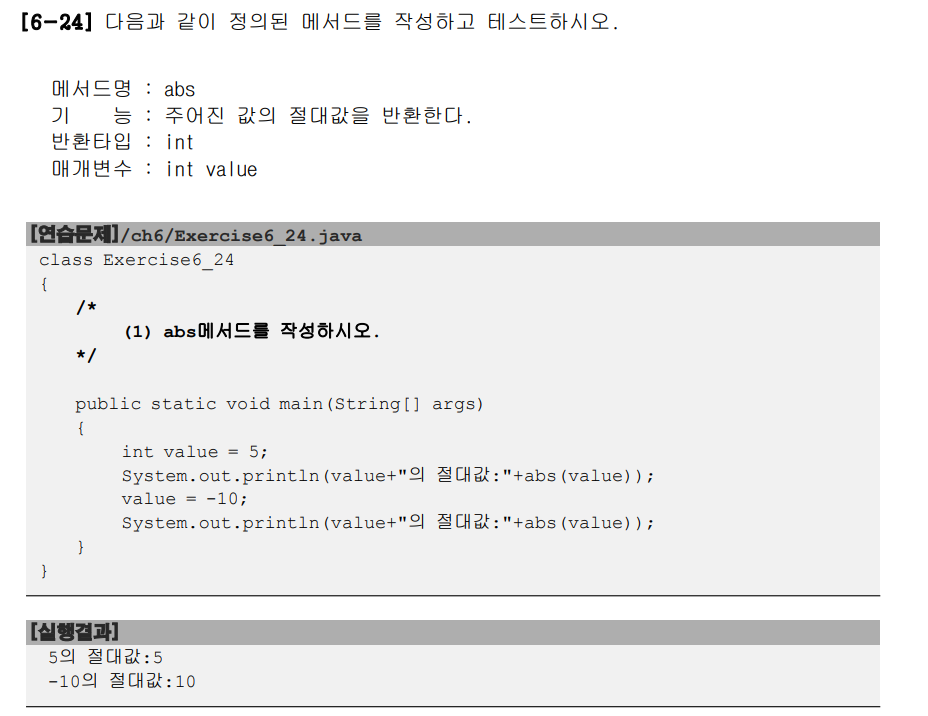
public class Exercise6_24 {
static int abs(int value) {
if(value < 0)
value = -value;
return value;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int value = 5;
System.out.println(value+" :"+abs(value));
value = -10;
System.out.println(value+" :"+abs(value));
}
}
삼항연산자를 이용해서 이런 방법도 있다.
package ch06;
public class Exercise6_24 {
static int abs(int value) {
return value < 0 ? -value : value;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int value = 5;
System.out.println(value+" :"+abs(value));
value = -10;
System.out.println(value+" :"+abs(value));
}
}반응형
'자바의정석' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자바의 정석 - 기초편] ch7-3,4 클래스 간의 관계, 상속과 포함 (0) | 2022.03.18 |
|---|---|
| [자바의 정석 - 기초편] ch7-1,2 상속 (0) | 2022.03.17 |
| 자바의 정석 ch06 연습문제(1) [6-1~6-12] (0) | 2022.03.11 |
| [자바의 정석 - 기초편] ch6-38~41 변수의초기화, 멤버변수의 초기화 (0) | 2022.03.10 |
| [자바의 정석 - 기초편] ch6-36,37 생성자 this(), 참조변수 this (0) | 2022.03.10 |