반응형
defaultParameter is only for "undefined"
// Logical OR operator ||
function printMessage(text) {
const message = text || 'Nothing to display';
console.log(message);
}
printMessage('Hello');
printMessage(undefined);
printMessage(null);
printMessage(0);
printMessage('');>> 출력 1번째 값 빼고 모두 'Nothing to display' 출력
Nullish coalescing operator ??
leftExpr ?? rightEx
null, undefined
undefined과 null 도 fasle
boolean false Nan, 0, -0 도 falsy
" , ' ,
const result = getInitialState() ?? fetchFromServer();
const result = getInitialState() ?? fetchFromServer();
console.log(result);
function getInitialState(){
return null;
}
function getInitialState(){
return 'Hiya from a';
}
text 는,,,
//Object Destructuring
const person = {
name: 'Julia',
age: 20,
phone: '01077778888'
}
// X BAD CODE!
function displayPerson(person) {
displayAvatar(person.name);
displayName(person.name);
displayProfile(person.name, person.age);
}ㄴ person.name 이 반복되어 있어 나쁜 코드 스멜이 난다.
// X STILL BAD CODE!
function displayPerson(person) {
const name = person.name;
const age = person.age;
displayAvatar(name);
displayName(name);
displayProfile(name, age);
}
object destructing 을 이용해보자!
// O GOOD CODE!
function displayPerson(person){
const { name, age } = person;
displayAvatar(name);
displayName(name);
displayProfile(name, age);
}
Spread Syntax
item 과 detail을 한꺼번에 묶을 수 있는 방법은?
// Spread Syntax - Object
const item = { type: 'C', size: 'M' };
const detail = { price: 20, made: 'Korea', gender: 'M' };
// X BAD CODE!
item['price'] = detail.price;
// X BAD CODE!
const newObject = new Object();
newObject['type'] = item.type;
newObject['size'] = item.size;
newObject['price'] = detail.price;
newObject['made'] = detail.made;
newObject['gender'] = detail.gender;
// X BAD CODE!
const newObject2 = {
type: item.type,
size: item.size,
price: detail.price,
made: detail.made,
gender: detail.gender
}
// O GOOD CODE! : 과거문법
const shirt0 = Object.assign(item, detail);
// O BETTER CODE!
//새로운 변수 업데이트 가능
cosnt shirt = {...item, ...detail, price:40};
// Spread Syntax - Array
let fruits = ['watermelon', 'orange', 'banana'];
// fruits.push('strawberry');
fruits = [...fruits, 'strawberry'];
// fruits.unshift('grape');
fruits = ['grape', ...fruits];
const fruits2 = ['watermelon', 'peach', 'pineapple'];
let combined = fruits.concat(fruits2);
combined = [...fruits, 'blueberry', ...fruits2];
Optional Chaning
bob과 anna가 있다.
anna는 일자리를 구했고, bob은 일자리를 구하지 못했다.
// Optional Chaning
const bob = {
name: 'Julia',
age: 20,
};
const anna = {
name: 'Julia',
age: 20,
job: {
title: 'Software Engineer',
},
};
// X BAD CODE!
function displayJobTitle(person) {
if(person.job && person.job.title)
console.log(person.job.title);
}
// O GOOD CODE!
function display(person) {
if(person.job?.title) {
console.log(person.job.title);
}
}
// O GOOD CODE!
function displayJobTitle(person) {
const title = person.job?.title ?? 'No Job Yet';
console.log(title);
}Template Literals
// Template Literals (Template String)
const person = {
name: 'Julia',
socre: 4,
};
// X BAD CODE!
console.log( 'Hello ' + person.name + ', Your current score is: ' + person.score );
// O GOOD CODE!
console.log(`Hello ${person.name}, Your current score is: ' + ${person.score}` );
// O GOOD CODE!
const {name, score} = person;
console.log(`Hello ${name}, Your current score is + ' + ${score}` );
// O GOOD CODE! FOR REUSE
function greetings(person) {
const { name, score } = person;
console.log(`Hello ${name}, Your current score is + ' + ${score}` );
}
Chaning
// Good Code
const result = items
.filter((num) => num % 2 === 0)
.map((num) => num * 4)
.reduce((a, b) => a + b, 0);
console.log(result);
async * await
//Promise -> Async/await
// X BAD CODE!
function displayUser(){
fetchUser() //
.then((user) => {
fetchProfile(user) //
.then((profile) => {
updateUI(user, profile);
});
});
}두 가지 이상의 promise를 연결해서 사용해야 할 때,
async 와 await을 이용하면 깔끔하고 순차적으로 확인할 수 있기 때문에 가독성을 높이고, 이해력을 높일 수 있다.
// O GOOD CODE!
async funciton displayUser() {
const user = await fetchUser();
const profile = await fetchProfile(user);
updateUI(user, profile);
}ㄴ 아직 모르는 부분........
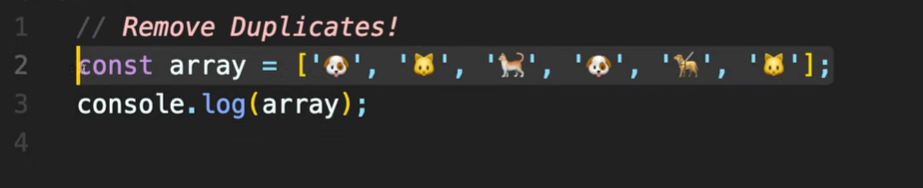
퀴즈 해결 시간은 3초 ㅋㅋㅋ
Q. 중복되는 동물들을 제거하는 배열을 만들어라!
A.
console.log([...new Set(array)]);[] 배열 안에 Set으로 array를 다시 정의한다.
Set은 ArrayList와 달리 중복된 값을 허용하지 않기 때문에, 중복된 값들을 제외한 배열을 보여준다.
Javascript API
.filter
.map
.reduce
반응형
'Javascript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Javascript] CDN이란? (Content Delivery Network) (0) | 2021.08.25 |
|---|---|
| [Javascript] 지도 API 사용하기 (0) | 2021.08.12 |
| [Javascript] onkeypress() / keyup, keypress, keydown (0) | 2021.07.29 |
| [Javascript] querySelectorById와 getElementBy 차이 (0) | 2021.07.23 |
| [Javascript] value, textContent, innerHTML, innerText 차이 (0) | 2021.07.23 |